Maximum and minimum sentences

The legal terms used on this page are explained in our jargon buster.
When deciding a sentence, a judge must first see whether minimum or maximum sentences have been set for the particular crime. Judges must also take account of any sentencing guidelines relevant to a case. If they do not follow these guidelines, they must give their reasons.
Legislation
In many cases, the law sets out the maximum sentence that can be given for a particular crime or offender. For example, a person convicted of threatening or abusive behaviour on indictment (more serious offences) cannot be sentenced to more than five years imprisonment, or a fine, or both. See the law.
In other cases, the law sets out the minimum sentence that must be given for a particular crime or offender. For example, if someone over the age of 18 is convicted in the High Court of a third drug trafficking offence, the law says that they must be sentenced to a minimum of at least seven years’ imprisonment.
Scottish law is mainly set out in Acts of Parliament (either from the UK Parliament or the Scottish Parliament), and in previous cases that have come before the courts.
Which Court
Criminal cases are dealt with in different courts depending on how serious they are. It is usually up to the procurator fiscal (the prosecutor) to decide what court a case will be heard in. Maximum penalties are set by law for each court a case will be heard in. A sheriff court can hear summary (less serious) or solemn (more serious) proceedings.
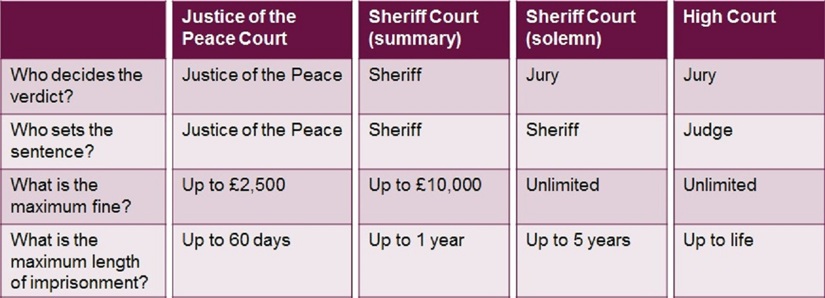
*community based sentences are available in all courts
If a sheriff in a solemn case decides that the maximum sentence at the sheriff court level isn’t high enough, they can send (remit) the case to the High Court for sentence. Justices of the Peace powers of punishment are limited to 60 days’ imprisonment or a fine of up to £2,500 or both. They can also disqualify drivers on a discretionary basis.
Guideline judgments by the High Court
Judges in the High Court, when it is sitting as an appeal court, have the power to make a decision in an appeal case that gives guidance to other judges about the appropriate sentence to use in similar types of cases. These judgments are known as ‘guideline judgments’. There are only a few of these in Scotland. For a full list and more information, see our web page using the link below.
Judges may also look at decisions made by other sentencing judges in similar situations, known as case law.

